Frontal labeling of warnings: a necessary policy to protect the right to health
The Ministry of Health published a bibliographic review document of front labeling options. The highest health authority in our country explicitly recommends the frontal labeling of warnings. It is urgent to turn those recommendations into public policies.
“Below, we offer a google translate version of the original article in Spanish. This translation may not be accurate but serves as a general presentation of the article. For more accurate information, please switch to the Spanish version of the website. In addition, feel free to directly contact in English the person mentioned at the bottom of this article with regards to this topic”.
In our country, according to the National Survey of Risk Factors 2013 (ENFR 2013, Ministry of Health of the Nation), 57.9% of the adult population is overweight, 34.1% have high blood pressure and the daily average of portions of fruits or vegetables consumed is 1.9 per person. Added to this is the fact that salt consumption is twice as much and added sugar is three times the maximum recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO). This situation demonstrates the need to formulate public policies that tend to reduce the consumption of products with critical nutrients and to improve the dietary habits of the population in order to reduce overweight, obesity and other noncommunicable diseases.
In this sense, the World Health Organization has recognized a series of policies of proven effectiveness to prevent obesity, such as the restriction of advertising of unhealthy foods and beverages, a front labeling of food warnings, fiscal measures, among others. In addition, numerous human rights committees have recommended the implementation of food policies as a necessary element to protect the right to health of people.
Thus, in the concluding comments made in November of the current report to Argentina, the Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights recommended “Taking effective measures to discourage the consumption of food and beverages harmful to health, including by increasing the tax on sugary drinks, strengthening the regulation of the Argentine Food Code in terms of front labeling of foods, including information on sugar in products, and implementing restrictions on the advertising of foods and beverages harmful to health, particularly those intended for children”. In the same sense, the Pan-American Health Organization (PAHO) proposes frontal labeling as one of its lines of action for the prevention of them because it facilitates the selection of healthier foods and encourages the industry to reformulate its products with the goal of making them healthier.
In Argentina there is no system of front labeling of foods established by law that informs consumers about high contents of critical nutrients (sugars, fats and sodium) nor is it mandatory to declare sugars in packaged products. For this reason and in accordance with the recommendations described, the National Program of Healthy Eating and Prevention of Obesity worked to promote a debate and positioning of the National Commission of Healthy Eating and Prevention of Obesity, regarding the type of frontal labeling to recommend for the Argentina. In this framework, 16 participating institutions voted on what type of frontal labeling and which nutrient profile system to adopt: 9 proposed warning labeling, 2 suggested Nutri-Score, 1 proposed the combination of both (warning plus Nutri- Score), 1 institution recommended a system of its own, 2 suggested the GDA with colors of the traffic light and 1 institution proposed “anyone other than the GDA”. Regarding the nutrient profile, 9 institutions proposed a profile of PAHO or an adaptation of it.
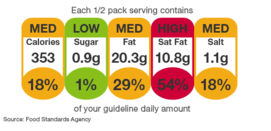
The researches examined showed the ineffectiveness of the GDA (daily feeding guides) labeling – which reports recommended percentages of daily energy or nutrient intake per serving or product – since it is generally not understood by adults or by adults. children, it takes a lot of time and is confusing even with nutritional knowledge. Despite this, this system was recommended by the Coordinator of the Food Products Industries (COPAL), an institution that declared conflicts of interest to receive financing from the industry, and by the Ministry of Production and Labor (Secretary of the Government of Agribusiness and Secretary of Commerce).
On the other hand, numerous publications explain why the frontal labeling type traffic light and the summary systems (Nutri-Score and HSR) do not influence the purchasing behavior, which is why they would not be appropriate to help the consumer in the choice of products healthy The semaphore problems to achieve this purpose, are linked to the confusion that generates in the nutritional interpretation. It has been proven that there is a compensation effect between green and red colors when they occur in the same product at the same time and that reporting on unfavorable attributes has a greater effect on the purchase decision than reporting favorable attributes. Therefore, we compare the confusion generated by the traffic light front labeling with the confusion that would generate for a motorist, that the traffic light keep its red and green lights on at the same time.
On the other hand, Nutri-Score classifies foods and beverages according to five categories of nutritional quality and a score is established assigning the product a letter and a color. The most nutritionally favorable product obtains a green “A” score and the nutritionally less favorable product obtains a red “E” score. Research showed that although it was useful to classify how healthy foods are, it was not effective to improve purchasing behavior due to the complexity generated by the combination of 5 letters with a gradient of 5 colors ranging from red to green. In addition, a food may have a high sugar content, but if it has fiber, its assessment will not necessarily be red. In this way, the consumer does not know that the food has a high content of sugar, fat or sodium, information that was shown to influence the purchasing behavior. This type of front labeling was recommended by the Center for Studies on Food Policy and Economics (CEPEA) and Center for Studies on Child Nutrition (CESNI), both institutions that expressed conflicts of interest in receiving financing from the industry.
From FUNDEPS, we supported the recommendations made by 9 of the participating institutions, including the Health Ministry, who spoke in favor of the frontal warning labeling and the nutrient profile of OPS. Indeed, numerous studies have shown that this system is the most effective in identifying products with a high content of critical nutrients (sugars, saturated fats and sodium), provides better information for the consumer, in a shorter time and favors the selection of food. healthier. Likewise, this type of labeling is prioritized because it is the most understood by children and adolescents and people of lower educational level, which is central to contemplate the perspective of inequity in public policy and protect especially the groups in the most vulnerable situations. vulnerability, those who suffer the most from obesity, malnutrition and chronic diseases in general.
On the other hand, the Government Health Secretariat recommended that “the frontal labeling system be implemented in a mandatory and gradual manner. Progressive implementation could be useful to give both consumers and industries time to adapt to changes. It is also proposed to accompany the strategy of front labeling with communication and awareness campaigns so that the population understands the labeling and has more information on nutrition and healthy eating. In addition, it is recommended that front labeling be used as a tool to define other healthy eating and obesity prevention policies. Thus, all those foods and beverages with a critical nutrient in excess, as established by the frontal labeling system, are subject to marketing restrictions, are excluded or are included in small quantities in social plans with a food component and are not offered in establishments. schoolchildren or community kitchens. “
We consider that the technical recommendations of the Ministry of Health for the design of food labeling policies are adequate to protect the right to health of the population. In effect, the warning labeling supplies the necessary information on critical nutrients in excess, whose consumption is sought to be reduced. Thus, it protects consumers in order to make informed decisions, and contributes to the prevention of noncommunicable diseases related to inadequate nutrition. In this context of the growth of chronic noncommunicable diseases linked to an inadequate diet, it is urgent that the recommendations of the Ministry of Health become public policies that enable effective protection of health.
More information
Nutritional front labeling of food
Author
Slavenka Zec
Contact
Agustina Mozzoni, agustinamozzoni@fundeps.org